The opioid crisis has reached epidemic proportions. To combat it, the first step is acknowledging the problem. Get the facts about what’s happening and get up to speed on why we the people must come together to make a meaningful difference.
The UnTOLD Story
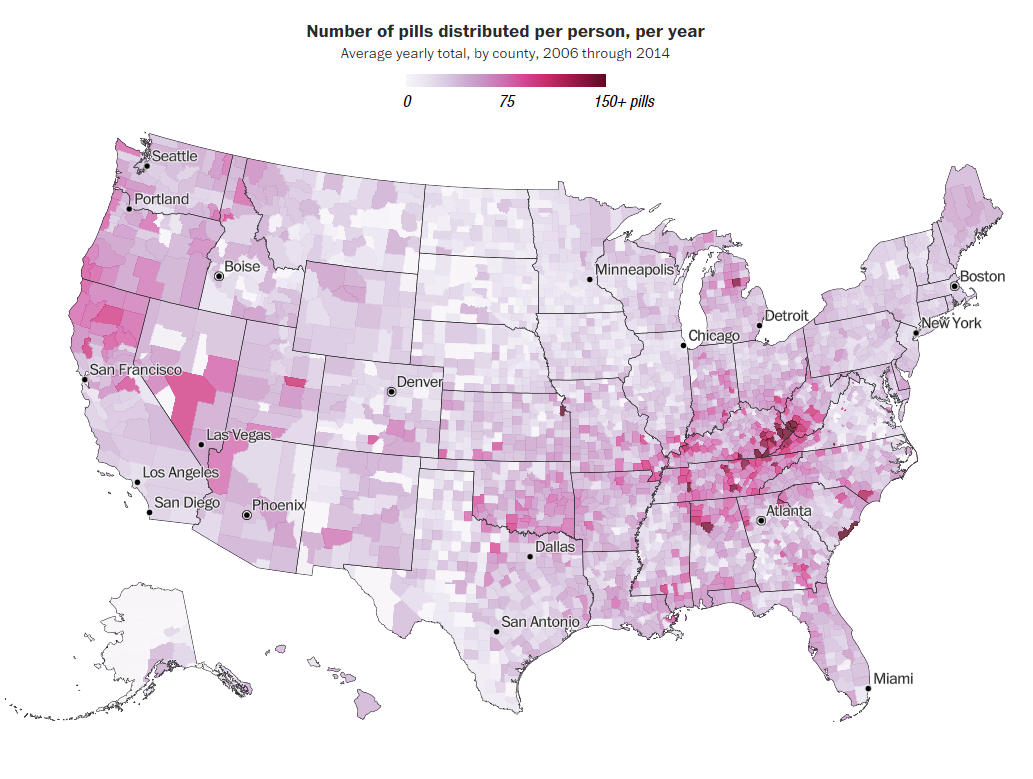
As part of the largest civil action in U.S. history, the secrecy of details surrounding the rise and proliferation of the opioid epidemic has finally lifted. A U.S. District judge ordered information from the ARCOS (Automation of Reports and Consolidated Order System) database, compiled and monitored by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), be released, giving us a real look into the depth of this crisis. And it’s mind-blowing.
100 billion opioid pills — yep, that’s billion with a “b” — were distributed in the U.S. from 2006 through 2014. That’s 32 pills for every adult and child in this country … every year. Right in our backyards, Leavenworth, Kan., was among the areas hardest hit. In the county during this window of time, 125,795,980 pain pills were distributed, or the equivalent of 186 pills per person per year.
Kansas Data
Missouri Data
Shocking Statistics
The opioid epidemic is considered the deadliest drug crisis in American history. The numbers will surprise you.
$631 billion
66%
Prescription and illicit opioids accounted for 75 percent of all drug overdose deaths nationwide in 2020
632,331
Between 1999 and 2016, there were more drug poisoning deaths (632,331) than the total American military and civilian deaths during World War II (418,500)
75%
3 out of 4 Americans who use heroin say their heroin addiction began with use of prescription opioids
No. 1
Drug poisonings are the leading cause of unintentional injury death in the U.S.
Every 8 minutes
There were 68,630 opioid-involved overdose deaths in 2020. That’s an average of 188 deaths per day nationwide — 1 every 8 minutes.
10.1 million
10.1 million Americans misused prescription opioids in 2018
5%
The U.S. consumes the majority of prescription opioids in the world — but only makes up 5% of world population
247,000
1 in 7
2.7 million
8x
Overdose deaths involving opioids, including prescription opioids, heroin, and synthetic opioids (like fentanyl), have increased by more than eight times since 1999
CAUTION: SYNTHETIC OPIOIDS
The opioid epidemic is being increasingly exacerbated by fentanyl, a synthetic opioid. Overdose deaths involving fentanyl are increasing at an alarming rate: More than 56,000 people died from overdoses involving synthetic opioids in 2020 alone. In Kansas, synthetic opioid overdose deaths, mostly caused by fentanyl, increased by 130% from 2019 to 2020.
The facts about fentanyl
Via CNN Health
Drug overdose deaths top 100,000 annually for the first time, driven by fentanyl, CDC data show
Sure, America has acknowledged the problem. And measures have been taken to limit prescription opioids in the marketplace. But the crisis has continued to morph and overdose deaths have soared. The Covid-19 pandemic and the rise in use of fentanyl have both been key contributors.
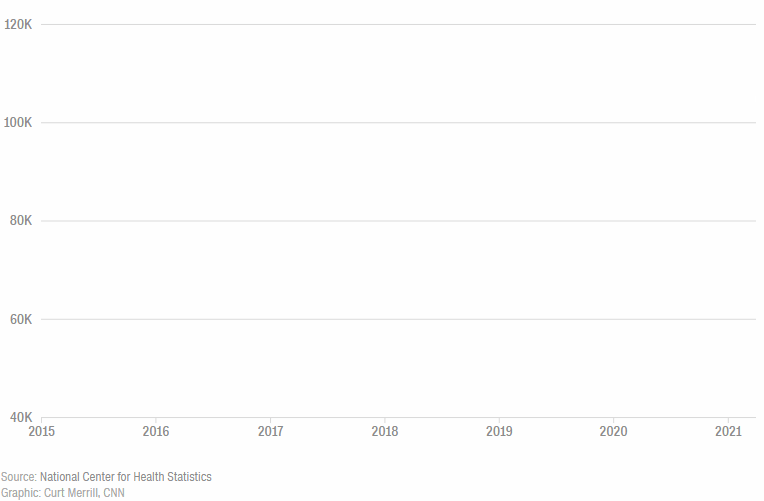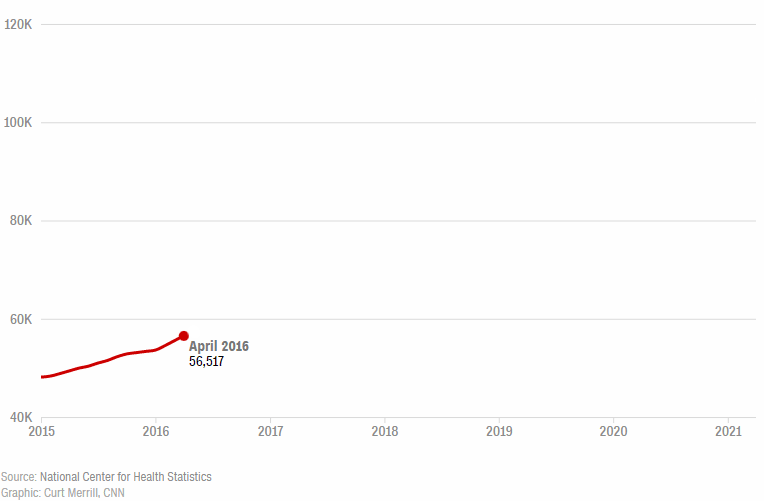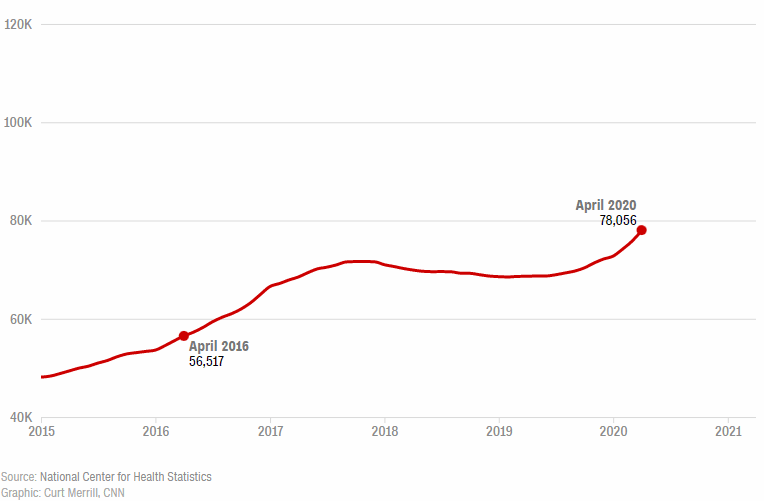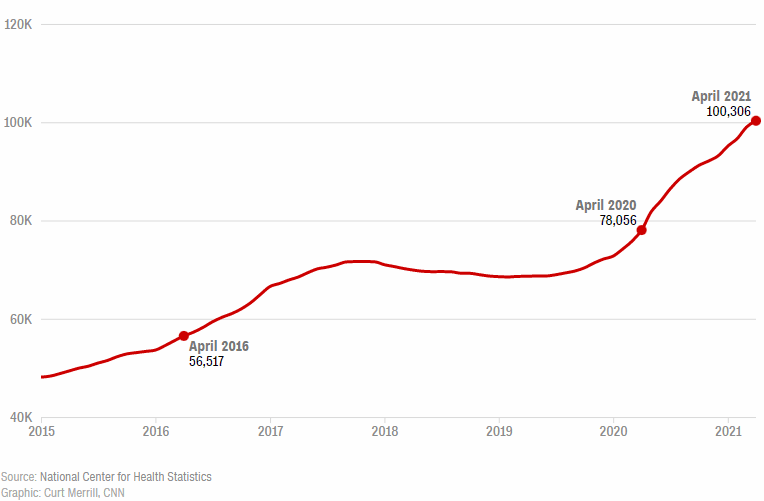
Here. There. Everywhere.
Opioid abuse has trickled down from adults to teens to pre-teens.
Kids believe it won’t happen to them. Parents believe it won’t happen to their kids. No one is invincible when it comes to opioids. Denial is not an option: Parents and teens must take notice of the risks of opioid abuse and take responsibility to prevent it.
“The obsession will not cease. I make myself sick with craving…. How can I be so completely obsessed with something so innately evil, destructive, costly, and all-powerful?”
— Alexa Lamoureux, who became addicted at age 19 and died of an overdose at age 28. Her mother created the memorial site LearnFromLexi.org to educate parents and young people about the truth of addiction
As the opioid crisis evolves, so does the fentanyl overdose problem. It is not “out there.” It’s here. In our schools. Among American teens, fentanyl-related overdose deaths rose 350% from 2019 to 2021, according to a new study of data from the CDC.
Fentanyl killed their boys. Now these KC area parents are on a quest to save lives
Kansas City Star, April 25, 2022
Hard-Hit Missouri
1 out of every 65 deaths were due to opioid overdose in Missouri in 2017
The National Institute on Drug Abuse reported that Missouri had 952 opioid overdose deaths in 2017. Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid that is 100 times stronger than morphine. Synthetic opioids including fentanyl accounted for 618 fatalities in 2017 — an elevenfold increase from 56 deaths in 2012.
38% of fatal overdoses happen when the user is alone, according to the Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services
Don’t let someone you love become a statistic: Monitor. Lock up. Dispose.


Kansas Governments Take Action
More than 2,600 parties nationwide are suing the opioid industry as a way to recoup funding that local governments have spent in response to the opioid epidemic. On that list are 28 governments in Kansas, including Johnson County, Leavenworth County and the Unified Government of Wyandotte County/Kansas City, Kan.
When Legal Turns Lethal
Addiction is a complex disease of the brain and body. It disrupts regions of the brain that are responsible for reward, motivation, learning, judgment and memory. It damages various body systems. It shatters families, relationships and neighborhoods. And it often starts with prescription drugs prescribed for specific pain.
In addition to the work being done by mothers and fathers, police forces, judges, politicians and communities to combat this crisis, every individual who has access to opioid pills needs to monitor, lock up and dispose of medication properly to ensure that an unintended deal doesn’t go down on your watch … and unexpected consequences don’t turn deadly.

